Water cooled backplane Simply put, the water-cooled backplane is to install a "cold water plate with cold circulation" behind the cabinet. The summary is as follows: the unit is mainly composed of a cold water distribution controller, a backplane heat exchanger, etc., and the cold water source is provided by the public cold water supply system of the computer room (cold water Distribution unit) Built-in heat exchanger, water pump, control valve, and temperature, pressure, humidity and other sensors to obtain accurate flow, pressure, temperature, humidity and other data. Through a unique algorithm, the two-stage circulation of cooling water is precisely controlled. From the backplane heat exchanger to maximize the elimination of the heat generated by the server, the water-cooled backplane adopts a fanless design, no power demand, no energy consumption, and noise reduction. Its dynamic, accurate and intelligent cooling technology can reduce cooling energy consumption. cost. Efficient and accurate heat exchange reduces the requirements for air conditioning in the computer room and avoids the impact of air conditioning failures.
Refrigerator type refrigeration-liquid cooling package This new modular refrigeration solution belongs to the "refrigerator-type refrigeration". A liquid cooling package (LCP) is installed on the side of the closed case. The hot air circulates out cold air through the liquid cooling package to directly cool the equipment. This new modular refrigeration solution takes into account various parameters such as temperature, humidity, operating speed, air flow, airflow direction, and power loss, and provides various cooling solutions, including a cabinet liquid cooling system and a high-efficiency liquid cooling system directly facing the CPU. The LCP (liquid cooling package) liquid cooling system of the microenvironment concept is used, and the hot spots are effectively cooled by water cooling, which can significantly reduce energy waste.

Industrial automation control mainly refers to the use of computer technology, microelectronics technology, and electrical means to make factory production and manufacturing more automated, efficient, precise, and controllable and visible. As the carrier of industrial control, industrial control machine requires high stability and special attribute requirements for continuous operation.
The heat dissipation requirements of industrial computers also need to be efficient and stable. Poor heat dissipation can easily lead to machine failure or system instability, which has a very bad impact on the industrial production environment. In view of the characteristics and requirements of the industrial control industry, our company adopts more fanless cooling solutions according to different customer system structures.
The heat dissipation performance of the water-cooled radiator is to maintain the normal operating temperature of the computer chip, which has become the focus of the research on the cooling problem of the data center. This paper takes the comprehensive coefficient F of the water-cooled heat sink and the chip temperature as the target parameters, and uses the orthogonal test method to determine the performance of the radiator. The thickness of the substrate, the position of the channel (located on the substrate), the number of channels and the width of the channel have been optimized, and the best combination for different needs is the F index and T index radiator. The results show that when the volume flow of cooling water is 0.4 L/min, when the inlet temperature is 20℃, the heat dissipation limit heat flux density of the T index and F index radiator are 78 W/cm~2, 65 W/cm~2 respectively. And from the temperature distribution and total The thermal resistance analyzes its heat dissipation performance in two aspects. The temperature gradient and total thermal resistance of the T-index radiator are lower than the F-index radiator, indicating that the T-index radiator is better than the F-index radiator; but under different volumetric flows, The pressure drop of the F index radiator is lower than that of the T index radiator. When the heat flow density of the chip is 65 W/cm~2 or less, the fluid flow effect in the F index radiator channel is better and can meet the heat dissipation requirements of the data center server , And higher heat flux density should choose T index radiator for cooling,
In order to meet the heat dissipation requirements of data center servers, a water-cooled heat pipe radiator was designed to dissipate the heat of the server’s CPU, and a server test platform was built to test the performance of this radiator. Under the conditions of different CPU load rateη, ambient temperature Ta, and water inlet temperature Tw, an experimental study was carried out on a server with a water-cooled heat pipe radiator, and the temperature change law of the server CPU was obtained. The experimental results show that the water-cooled heat pipe radiator has higher heat dissipation efficiency than the traditional air-cooled radiator, and the thermal resistance of the radiator is only 0.0704℃/W. The most important parameter that affects the heat dissipation effect of water-cooled heat pipe radiators is the inlet water temperature, and the environmental temperature has a relatively small effect on the temperature of the CPU. Therefore, by increasing the ambient temperature, the heat load of the air conditioning equipment in the data center can be reduced to achieve the purpose of energy saving.
Deploying liquid-cooled servers will not increase data center costs
Liquid cooling, as the name suggests, liquid is injected into the server to take away the heat from the server through heat and cold exchange. At present, Sugon's use of liquid cooling technology will increase the cost of the corresponding server by about 30% to 40%. However, this will not increase the construction cost of the data center.
"The heat of the heating component CPU and some power modules account for 70% of the server's heat. The use of liquid cooling technology can reduce the investment of 2/3 of the capacity of the air conditioner." Shen Weidong pointed out that the compressor is removed from the liquid cooling system, which is better than the air conditioner system. Significantly reduced costs can reduce the initial investment in data center infrastructure.
If liquid-cooled servers are introduced instead of building a new computer room, the investment in liquid-cooled chillers and air-cooled air-conditioning systems shall be comprehensively assessed. The basic investment required for liquid-cooled servers still has advantages for air-cooled systems.
Liquid cooling refers to the use of liquid as a cooling medium to dissipate heat for electronic equipment, which is mainly different from the current commonly used air cooling (air is used as a cooling medium to dissipate heat).
Liquid cooling is mainly divided into "indirect contact type" and "direct contact type".
Indirect contact type: the cooling liquid does not directly contact the heating device, the main heating device is fixed on the cold plate, and the liquid flowing through the cold plate flows in the designed liquid cooling radiator, and the cooling method takes away the heat through circulation. According to whether there is phase change, it is divided into: single-phase indirect liquid cooling; two-phase indirect liquid cooling.
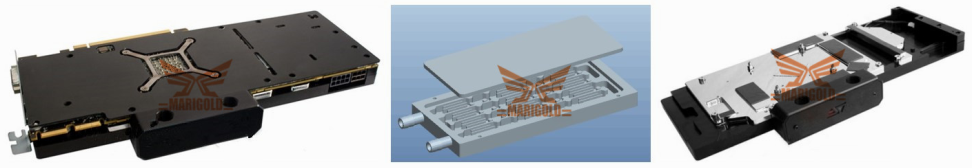
With the rapid development of the information society, the construction of data centers continues to accelerate. While the computing power of the server continues to increase and the integration degree continues to increase, it also faces problems that hinder its development. The heat dissipation system of a server with high heat flux has problems such as large energy consumption and insufficient heat dissipation capacity. In order to meet the working needs of servers with high heat flux, this paper proposes a water-cooled heat pipe radiator solution. Through the water-cooled heat pipe radiator installed inside the server, the heat inside the server is exported to the water-cooling plate outside the server through the heat pipe. Among them, it is cooled by the cooling water of the pipeline system in the data center. The paper describes the manufacturing scheme and specific process flow of the water-cooled heat pipe radiator, and analyzes the thermal resistance composition of the radiator structure. It is found that the thermal resistance of the heat pipe and the water-cooling plate is the key parameter that affects the performance of the radiator. Optimize the heat transfer performance of the heat pipe and the water-cooled plate. For the heat pipe, by comparing the change law of the limit heat transfer power, thermal resistance and working temperature range of the heat pipe under different wicks and liquid injection rates, it is found that for long heat pipes with gravity-assisted working fluid reflux, high permeability should be used. , The liquid wick structure with low liquid flow resistance; in the range of 80%-160% liquid injection rate, as the liquid injection rate increases, the limit heat transfer power of the heat pipe increases. But at the same time, a larger injection rate will cause blockage at the condensing end of the heat pipe and increase the thermal resistance of the heat pipe. Therefore, under the premise of meeting the heat transfer power requirements, the low injection rate should be used as much as possible; When the cooling temperature is in the range of 10℃-50℃, the limit heat transfer power of the heat pipe decreases with the decrease of temperature. Because the viscosity of the heat pipe working fluid increases at low temperatures, the reflux resistance of the working fluid increases, so the heat pipe is at 10 At a cooling temperature of ℃, there is only a limit heat transfer power of 5-20W. For the water-cooling plate, the Fluent software was used to compare the water-cooling plates of three different channel structures, and the temperature distribution, flow pressure loss, etc. were compared. It was found that the series-parallel channel structure has better performance than the simple series structure channel. The heat transfer effect and resistance characteristics. Finally, I tested the application of the optimized water-cooled heat pipe radiator in the actual server, and compared it with the air-cooled radiator, and found that when the ambient temperature is Ta=25°C, the water-cooled heat pipe radiator is used. It can reduce the full load temperature of the CPU by about 20°C. Under the rated water cooling conditions, the total thermal resistance of the radiator is 0.0843°C/W. After the above analysis, it is found that the use of water-cooled heat pipe radiator can effectively dissipate the heat of the server, and it runs well in actual applications. The radiator structure proposes a feasible method for improving the heat dissipation efficiency of the data center.
How to strengthen the heat dissipation performance of the water-cooled radiator to maintain the normal operating temperature of the computer chip has become the focus of the research on the cooling problem of the data center server. This paper takes the comprehensive coefficient F of the water-cooled heat sink and the chip temperature as the target parameters, and uses the orthogonal test method to heat the heat The thickness of the substrate, the position of the channel (located on the substrate), the number of channels and the width of the channel have been optimized, and the best combination for different needs is the F index and T index radiator. The results show that: when the cooling water volume When the flow rate is 0.4 L/min and the inlet temperature is 20℃, the heat dissipation limit heat flux density of the T index and F index radiator are 78 W/cm~2 and 65 W/cm~2 respectively. And the temperature distribution from the bottom of the radiator Analyze its heat dissipation performance from the two aspects of total thermal resistance. The bottom temperature gradient and total thermal resistance of the T-index radiator are lower than the F-index radiator, indicating that the T-index radiator is better than the F-index radiator. The pressure drop of the F-index radiator is lower than that of the T-index radiator. When the heat flow density of the chip is 65 W/cm~2 or less, the fluid flow effect in the F-index radiator channel is better and can meet the requirements of data center servers. Heat dissipation requirements, and higher heat flux density should choose T index radiator for cooling,

In addition, in response to users’ concerns about liquid-cooled server liquid leakage, Sugon has investigated a variety of quick-plugging solutions, and has done a large number of experiments in the past 3 years to verify the reliability of its liquid-cooled servers in this respect. It is reported that the mass-produced TC4600E-LP liquid-cooled server has been applied to the "Earth Numerical Simulation Device" prototype system of the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. In the future, liquid cooling may trigger subversive innovation in the industry. TC4600E-LP is a cold plate liquid cooling Server, it is a kind of liquid cooling mode in the industry, and has not yet touched the change of the physical appearance of the server. And another liquid cooling mode-immersion, may bring subversive changes in the server architecture. "The current cold plate liquid cooling technology is unlikely to change the existing physical form of the server. It just replaces the original CPU heat sink with a cold plate. This step is relatively easy to implement." the immersion type is the "immersion version." "The cold plate type is actually an intermediate alternative, and the immersion type is the final result
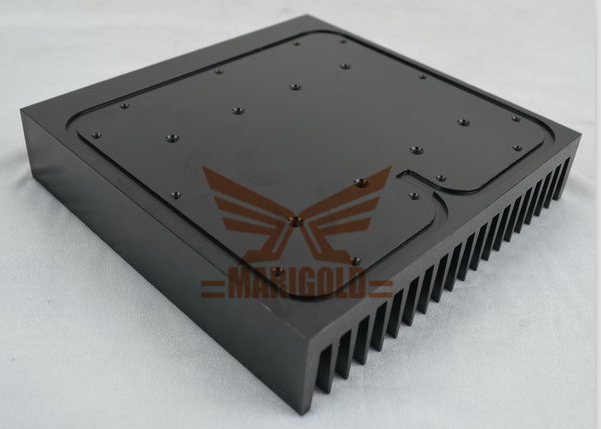


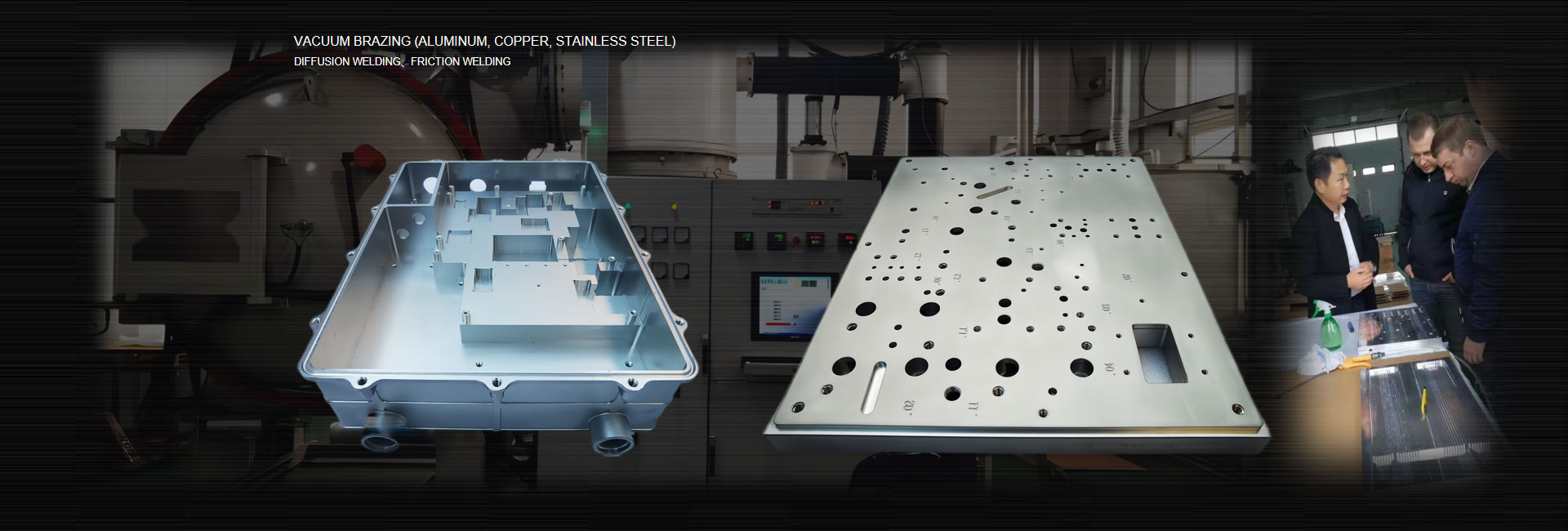
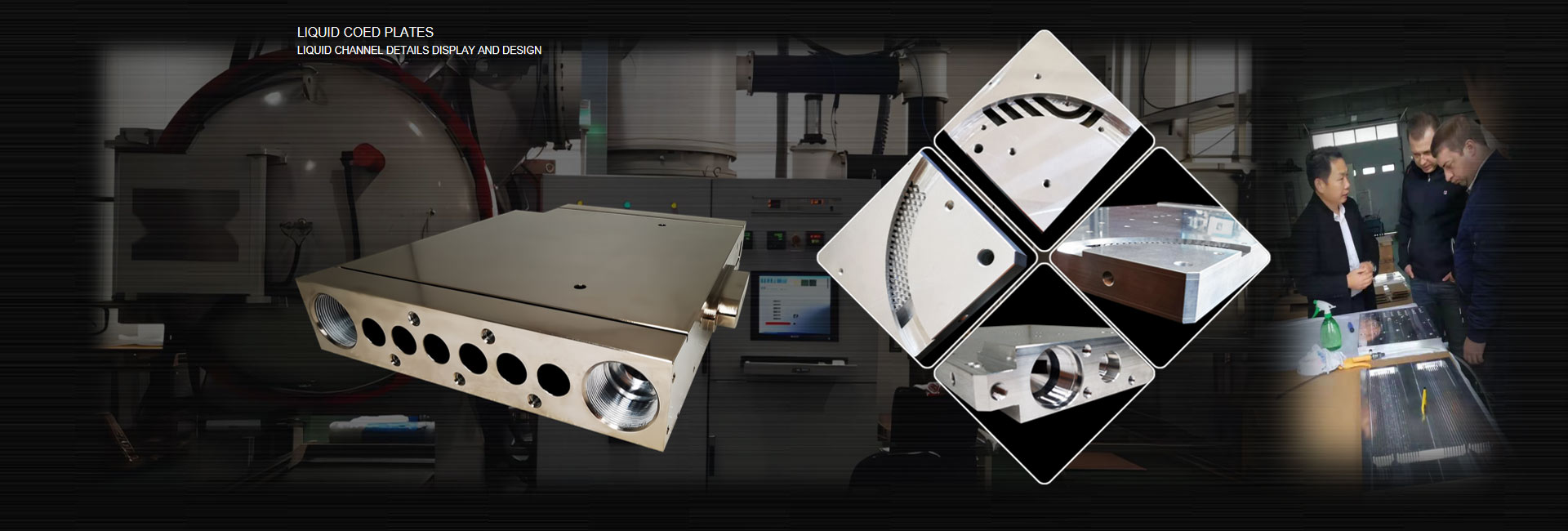
Vacuum brazed water cooling plate & spade fins & stamping fins & extruded fins