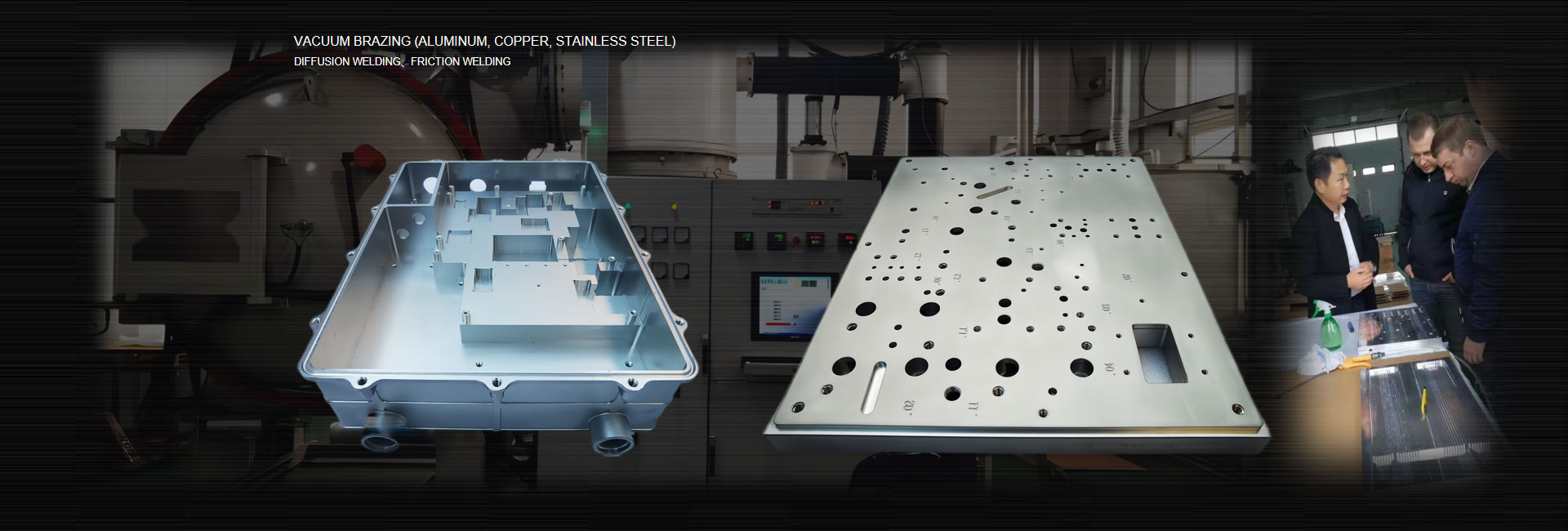
1, Rail transit water-cooled heat dissipation method, cooling can ensure the stability of thermal resistance, which method is more suitable, structure, reliable operation, and cost are the focus of consideration. Each method has advantages and disadvantages. The figure below is based on power consumption. Parameters and ranges can be determined by reference
2. The thermal resistance is an important indicator to measure the heat dissipation capacity of the radiator. The focus of the thermal design of the IGBT heat pipe radiator is the calculation of the thermal resistance of the radiator. When selecting, first determine the cooling method according to the power consumption of the original device, and the parameter is determined The range can refer to the figure below to select a high-power heat pipe radiator
The characteristics of the IGBT module air-cooled radiator. The air-cooled radiator is characterized by high heat dissipation efficiency, low cost, high reliability, simple structure, and convenient maintenance. The traditional air-cooled type has always been subject to the process, mold, and mold of the radiator. The level of processing capability has not made great progress in the heat dissipation capability, and its application is only suitable when the heat dissipation power is small and the heat dissipation space is large. Even so, the application of air-cooled radiators in power electronic devices is quite extensive and common.

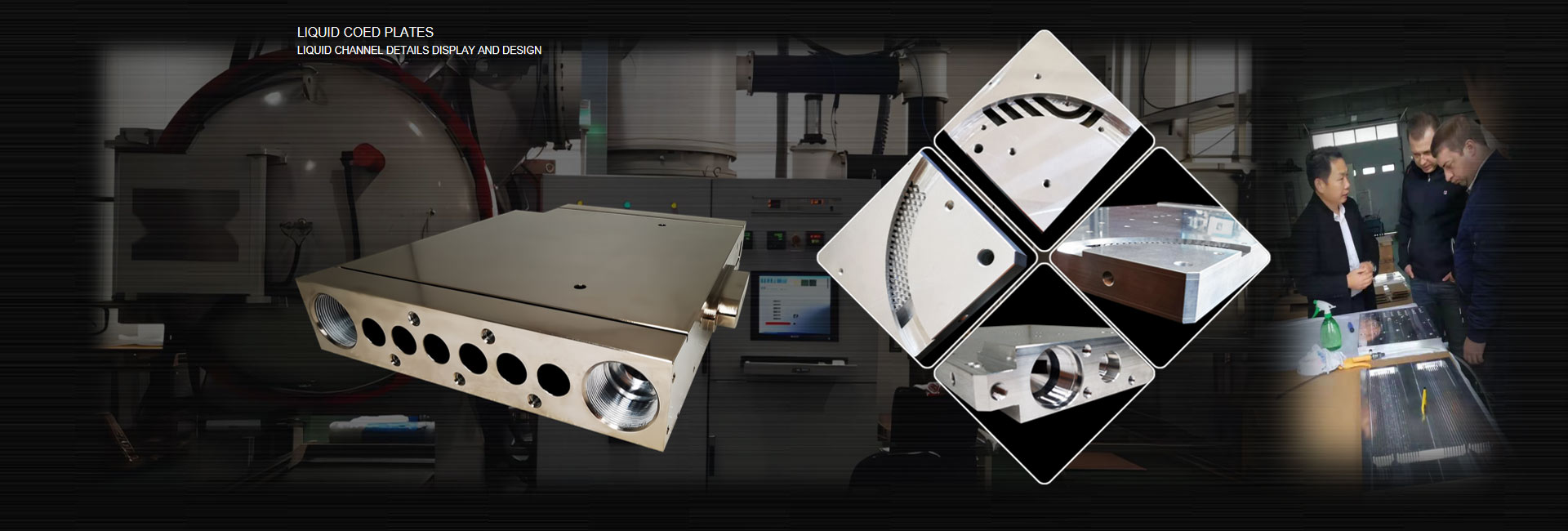
The coolant uses a mixed solution of water and ethylene glycol. The coolant brings the heat generated by the IGBT to the heat exchanger, drives the fan, and takes away the heat of the internal coolant to stabilize the IGBT in a constant temperature range to ensure normal The needs of the job. It adopts high-efficiency heat dissipation design and has the advantages of small size and light weight.
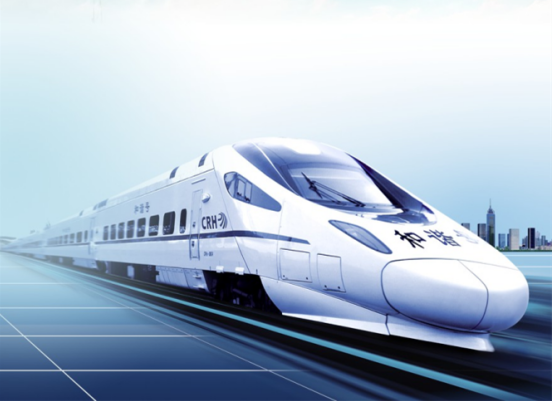
High-power heat pipe heat sink for rail transit IGBT converter
Aluminum radiator has the advantages of light weight, good heat transfer capacity, simple processing technology and low production cost. It is an effective solution for the lightweight of rail transportation equipment cooling system. It mainly introduces the structural characteristics of rail transportation equipment cooling system aluminum radiator, Application status and anti-corrosion improvement measures.
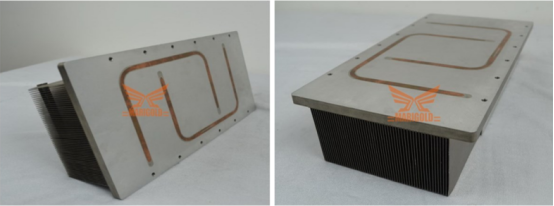
Heat pipe IGBT radiator Application areas: light rail, subway, high-speed train
With the rapid development of power electronics technology, and current electronic equipment's requirements for high-performance, high-reliability, and high-power components continue to increase, the degree of heat dissipation per unit volume is getting higher and higher, resulting in a sharp increase in heat and temperature . As the thermal drive causes more and more serious problems in mechanical, chemical, electrical and other aspects, which seriously restricts the quality and reliability of products, the heat dissipation problem of high-power components (IGBT modules) has become the current power electronic application field. Hot spot.

Heat pipe IGBT radiator Application areas: light rail, subway, high-speed train
Heat dissipation scheme for high-power electronic devices (IGBT module heat sink)
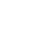
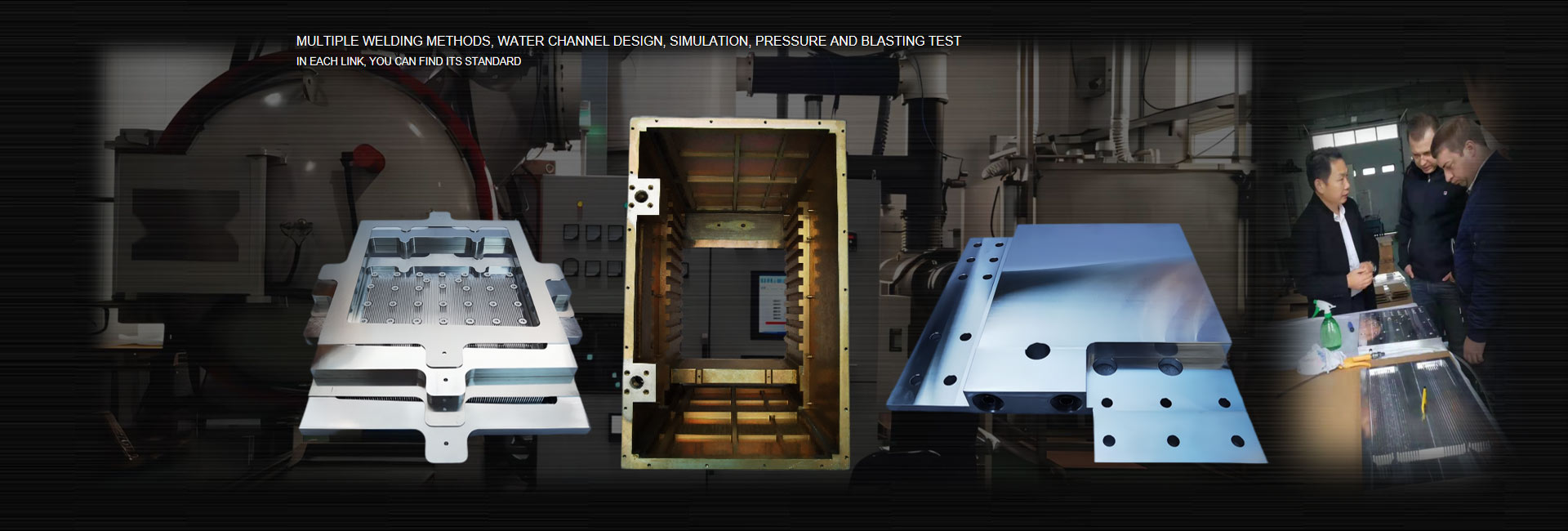
In the thermal design of electronic components, the choice of heat dissipation methods, and the testing, simulation, analysis, and optimization of them to obtain a structure with high thermal efficiency and low cost are essential for ensuring that the internal junction temperature of the power device is always kept within the allowable range during operation. It is particularly important within.
For high-power radiators, the working environment and the temperature changes on the original electronic components are different during air cooling. The relative temperature on the inlet side is relatively low and the wind speed is higher, and the temperature on the outlet side is higher and the wind speed is lower. For two electronic original devices on the same substrate, the temperature on the air outlet side is higher.

Heat pipe IGBT radiator Application areas: light rail, subway, high-speed train